The Complete Guide to Extracting Data from Bill of Lading (BoL) for Logistics Automation
Manual bill of lading processing costs logistics companies an average of 47 minutes per document and generates errors in 23% of shipments. For freight forwarders processing thousands of bills of lading monthly, this translates to hundreds of thousands in annual labor costs.
This does not include delays, compliance violations, and customer dissatisfaction from data entry mistakes. You can have several questions like:
- Are your teams losing hours daily to manual bill of lading data entry while competitors automate freight workflows?
- How many shipment delays could you prevent by eliminating human errors in shipper and consignee information?
- What would 90% faster customs clearance mean for your customer satisfaction and operational costs?
Bill of Lading OCR (Optical Character Recognition) technology uses AI and machine learning to extract data from bill of lading documents automatically. This process transforms scanned or digital BOL documents into structured, machine-readable data within seconds.
Leading logistics companies now process thousands of bills of lading daily with high accuracy and minimal manual intervention, significantly reducing operational costs while improving compliance and customer service.
Key Takeaways
- OCR technology extracts critical freight data including shipper details, consignee information, container numbers, and cargo descriptions from any bill of lading format
- Processing time reduces from 47 minutes to under 2 minutes per document with automated data extraction and validation
- AI-powered classification automatically identifies bill of lading types (ocean, inland, negotiable) and applies appropriate extraction rules
- Integration capabilities connect directly with TMS, ERP, and customs systems for real-time freight workflow automation
- Template-free processing adapts to different carrier formats without manual configuration or training requirements
- Multi-language support handles international shipping documents in 50+ languages for global logistics operations
- Compliance validation ensures extracted data meets GDPR, DPDPA, and customs authority requirements automatically
What is Bill of Lading Data Extraction?
Bill of Lading OCR refers to the application of optical character recognition technology to extract text and data from bills of lading documents. Bills of lading are legal documents issued by carriers that acknowledge receipt of cargo for shipment and serve as contracts between shippers and carriers.
This technology transforms physical or digital bill of lading documents into structured, machine-readable data through sophisticated document extraction processes. The extracted information includes shipper and consignee details, cargo descriptions, container numbers, freight charges, and shipping dates.
Modern OCR systems use artificial intelligence and machine learning to handle various document formats, handwritten signatures, and multi-language content.
Key Components of Bill of Lading OCR Technology:
- Document Image Processing – Enhances document clarity and corrects orientation for optimal text recognition
- Text Recognition Engine – Converts image-based text into machine-readable characters using neural networks
- Data Classification – Identifies specific bill of lading fields and organizes information by category
- Validation Rules – Cross-checks extracted data against predefined business logic for accuracy
The result is accurate, structured data ready for integration into freight management systems, eliminating manual data entry and reducing processing errors dramatically.
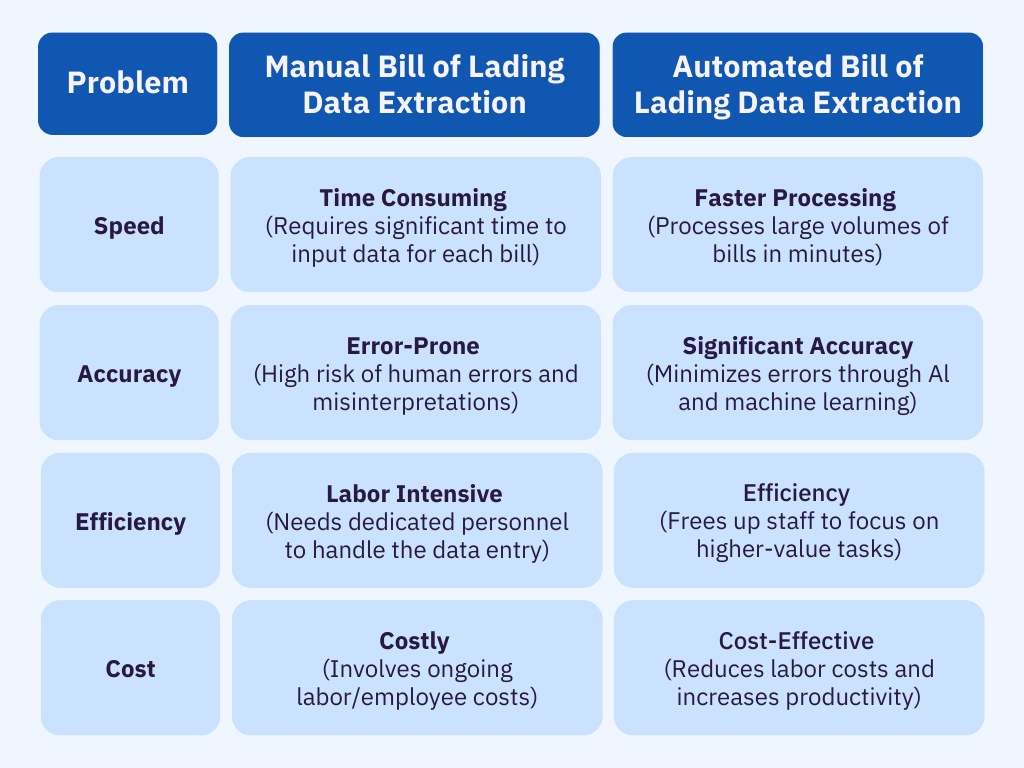
Manual vs Automated Bill of Lading Data Extraction
Essential Data Fields in a Bill of Lading
Comprehensive bill of lading data extraction captures all critical freight information required for logistics operations, customs compliance, and financial reconciliation:
Shipment Identification Data:
- Bill of lading number and carrier reference
- Booking confirmation and container numbers
- Seal numbers and equipment identification
- Purchase order and invoice references
Party Information:
- Shipper company name, address, and contact details
- Consignee destination information and delivery instructions
- Notify party details for shipment updates
- Third-party billing and payment responsible parties
Cargo and Container Details:
- Detailed cargo descriptions and commodity classifications
- Container types, sizes, and loading specifications
- Piece counts, weights (gross and net), and volume measurements
- Hazardous material declarations and special handling requirements
Transportation and Routing Information:
- Port of loading and final destination details
- Vessel names, voyage numbers, and sailing schedules
- Place of receipt and delivery locations
- Intermodal transportation arrangements
Financial and Commercial Terms:
- Freight charges breakdown and payment terms compatible with accounts payable processing
- Incoterms and delivery responsibility definitions
- Currency specifications and exchange rate considerations
- Insurance coverage and liability limitations
Compliance and Documentation:
- HS codes for customs classification
- Letters of credit and banking instructions
- Certificate requirements and inspection details
- Regulatory compliance declarations
Accurate extraction of these essential data fields enables automated data extraction workflows for customs filing, freight audit processing, and real-time shipment tracking without manual intervention.this data optimizes freight management, reduces errors, and ensures compliance with shipping regulations.
Must-Read Articles:
| How to Extract Data from Invoices? How to extract data from receipts? How to Extract Data from Insurance Policies? How to extract data from a Purchase Order? |
How Bill of Lading OCR Works: Technical Process Breakdown?
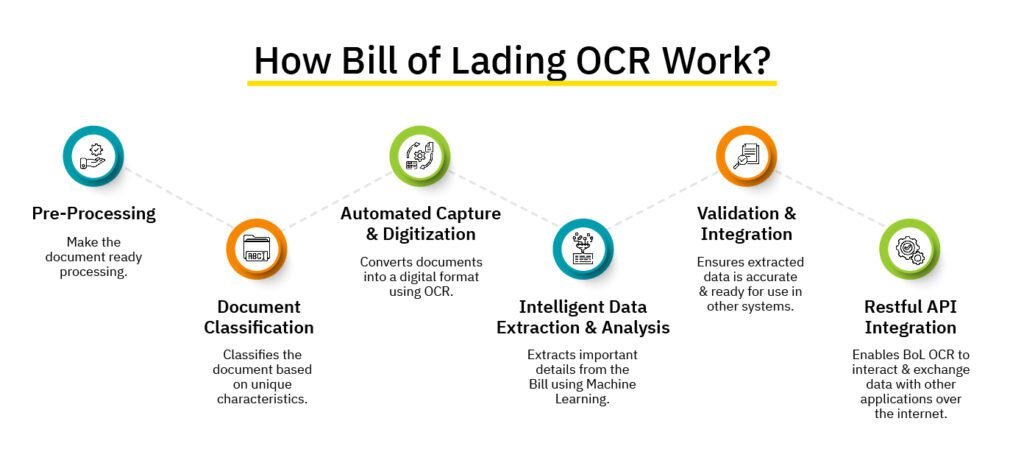
Modern bill of lading OCR operates through six automated stages that transform unstructured documents into actionable business data:
Stage 1: Document Import and Preprocessing
Bills of lading enter the system through email attachments, direct uploads, or API integrations. The preprocessing engine enhances image quality by removing noise, correcting skew, and normalizing resolution.
This stage handles common logistics document challenges like coffee stains, fold marks, and carrier stamps that typically interfere with text recognition.
Stage 2: Document Classification and Format Recognition
AI algorithms automatically identify the document type (ocean bill of lading, inland BOL, air waybill) and carrier format through advanced document classification techniques.
The system recognizes hundreds of different bill of lading templates from major shipping lines including Maersk, CMA CGM, and MSC without requiring manual template configuration.
Stage 3: Intelligent Field Extraction
Advanced OCR engines locate and extract specific data fields using spatial recognition and contextual understanding powered by intelligent document processing capabilities. The system identifies key logistics information including:
- Shipper and consignee names and addresses
- Container numbers and seal information
- Cargo descriptions and HS codes
- Port of loading and discharge details
- Freight charges and payment terms
Stage 4: Data Validation and Quality Control
Extracted information undergoes automated validation against shipping industry standards and business rules to ensure ocr accuracy meets enterprise requirements. The system verifies container number formats, validates port codes against official lists, and cross-checks weight calculations for consistency.
Stage 5: System Integration and Data Export
Validated data exports to target systems through RESTful APIs or direct database connections. Common integrations include TMS platforms (SAP TM, Oracle Transportation), ERP systems (SAP, NetSuite), and customs filing systems for automated declaration submission.
Stage 6: Continuous Learning and Accuracy Improvement
Machine learning models continuously improve accuracy by analyzing feedback from validation processes and adapting to new document variations through data automation techniques, ensuring consistent performance across diverse bill of lading formats.
This six-stage process typically completes within seconds per document, regardless of complexity or format variations.
Benefits of Using Automated Data Extraction from Bill of Lading
1. Better Consistency & Reduced Errors
Automated extraction eliminates human errors, ensuring accurate data capture and reducing discrepancies.
2. Improved Operational Efficiency
AI-powered Bill of Lading processing speeds up data extraction, reducing manual workload and optimizing workflows.
3. Higher Cost Savings
Cut down costs related to labor-intensive data entry and minimize financial losses due to manual errors.
4. Compliance & Risk Management
Automated data extraction ensures compliance with GDPR, DPDPA, and global trade regulations, reducing legal risks.
5. Scalability & Flexibility
Process thousands of BoLs simultaneously without slowing operations, even during peak shipping seasons.
6. Security & Audit Trails
Maintain a detailed log of extracted data with full audit tracking, ensuring transparency and security in freight processes.
Step-by-Step Guide to Extract Data from Bill of Lading Using KlearStack
Implementation Guide: Bill of Lading OCR API Integration
API Architecture and Technical Requirements
Modern bill of lading OCR APIs provide RESTful endpoints for seamless integration with existing logistics systems. The implementation process requires minimal technical overhead while delivering enterprise-grade processing capabilities.
Essential API Endpoints:
POST /documents/upload– Document submission and processing initiationGET /documents/{id}/status– Real-time processing status monitoringGET /documents/{id}/data– Structured data retrieval in JSON formatPOST /webhooks/configure– Event-driven notifications setup
Integration Workflow:
Step 1: Authentication and Environment Setup Configure API credentials and establish secure connection protocols. Most OCR providers offer sandbox environments for testing before production deployment.
Step 2: Document Upload Configuration Implement file upload mechanisms supporting PDF, JPEG, PNG, and TIFF formats. Configure automatic document routing from email systems or document management platforms.
Step 3: Data Processing and Validation Set up custom validation rules based on business requirements. Configure field mapping for seamless integration with existing database schemas and ERP systems.
Step 4: Webhook Configuration for Real-time Processing Establish webhook endpoints to receive processing notifications and extracted data. This enables immediate downstream processing without polling API endpoints.
Code Example – Python Integration:

Outstanding Features of KlearStack’s Bill of Lading OCR

1. Template-Free Processing
KlearStack’s AI-powered BoL OCR adapts to all Bill of Lading types without requiring manual template configurations, making it efficient for dynamic logistics environments.
2. Multi-Lingual OCR Support
Supports 50+ languages, allowing businesses with global operations to process BoLs in different languages accurately.
3. Bulk BoL Processing
Processes thousands of different types of Bill of Lading documents, eliminating manual workload and reducing document processing time.
4. Line-Item Data Extraction
Extracts detailed shipment data including shipper details, item descriptions, and financial records for accurate reconciliation.
5. Multi-Page Document Extraction
Handles multi-page BoLs seamlessly, ensuring every crucial data point is extracted, even from lengthy shipping documents.
6. Straight-Through Processing (STP)
Automates end-to-end Bill of Lading processing, reducing human intervention, speeding up workflows, and ensuring accuracy.
7. Seamless System Integration
Integrates with ERP, TMS, and financial management systems, ensuring extracted data flows directly into logistics operations.
8. AI-Powered Document Classification
Automatically classifies and categorizes BoLs, invoices, and purchase orders, reducing manual sorting efforts.
9. Automated Document Splitting
Identifies and separates BoLs from attached documents, improving processing efficiency and organization.
10. Rich Document Audit Engine
Validates extracted data against predefined business rules, flagging discrepancies for accurate compliance reporting.
11. Rules-Based Workflows
Set custom processing rules based on supplier, value, or product type, automating Bill of Lading document handling.
12. Self-Learning AI
Continuously improves accuracy by learning from past document extractions, enhancing efficiency over time.
Why Leading Logistics Companies Choose KlearStack
- 99% Data Accuracy – Zero human intervention, zero errors.
- Processes 1,000+ Documents Daily – Handles high-volume logistics effortlessly.
- Integrates with Your Existing Systems – No need to change your workflow.
Ready to eliminate manual Bill of Lading tracking? Experience how KlearStack can streamline your freight processes, reduce errors, and accelerate workflows.

Final Thoughts
BoL processing doesn’t have to be slow, error-prone, or costly. By automating data extraction, you improve operational efficiency, compliance, and cost-effectiveness.
Manual data entry is outdated. AI-powered automation is the future. If your logistics business handles high document volumes, KlearStack ensures accuracy, speed, and seamless integration — without the manual workload.
Don’t let outdated processes hold your business back. Automate Bill of Lading processing today with KlearStack!
Book a Free Demo Now
FAQs on Bill of Lading Data Extraction
Key details such as shipment details, consignee and shipper information, item descriptions, quantities, and transport information get extracted from a Bill of Lading.
The process of identifying and capturing relevant information from a Bill of Lading document is called data extraction from a Bill of Lading.
Two types of data extraction methods are – manual and automated data extraction software.


