Invoice Reconciliation: What It Is, How It Works, and Why It Matters?

Businesses lose 5% of their annual revenue to fraud, with incorrect invoice payments contributing to these losses [Association of Certified Fraud Examiners’ News Release]. These numbers point to a glaring need for strict financial controls.
A study by Ardent Partners shows that companies with mature invoice reconciliation processes have 80% fewer payment errors than those without such systems.
- Does your finance department spend hours fixing invoice payment errors?
- Are you worried about overpaying vendors due to duplicate invoices?
- Do you want to make your financial records more accurate and reliable?
These questions relate to common issues that financial teams face. Invoice reconciliation helps address these issues by making sure your payments match what you ordered and received.
This guide explains what invoice reconciliation is, how it works, and ways to make it more accurate.
Key Takeaways
- Invoice reconciliation is the process of matching invoices with purchase orders and receiving reports to verify payment accuracy.
- Regular reconciliation helps catch errors, prevent fraud, and maintain clean financial records.
- Two-way, three-way, and four-way matching are the main types of invoice reconciliation.
- Invoice reconciliation supports better cash flow management and helps build stronger vendor relationships.
What is Invoice Reconciliation?

Invoice reconciliation is the process of comparing invoices with purchase orders, receiving reports, and other financial documents to verify that the information matches accurately. It checks that what was ordered matches what was received and what was billed.
This accounting practice helps businesses confirm that they only pay for goods and services they actually ordered and received, and at the agreed-upon prices. The process compares details like product descriptions, quantities, prices, and terms across multiple documents.
Invoice reconciliation serves as a way to find and fix errors before they cause financial issues. It helps maintain the accuracy of financial records, prevent overpayments, and detect potential fraud.
For example, if an invoice shows a charge for 100 items but your receiving report shows only 80 were delivered, reconciliation would flag this issue before payment.
Every business — whether small or large — uses invoice reconciliation to check if:
- The items listed were actually received.
- The price and quantity are correct.
- No duplicate charges are present.
Without reconciliation, a business risks payment errors, disputes, and unreliable financial reporting.
A strong reconciliation process also helps businesses manage cash flow more precisely by making sure they pay the right amounts at the right times.
This lets companies make better financial plans and avoid wasting money on incorrect payments.
Steps involved in Invoice Reconciliation?

The invoice reconciliation process follows a specific flow to make sure all financial records match up correctly.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it works:
1. Gathering Documents
The first step is to collect all needed documents in one place. These typically include:
- Invoices from vendors
- Purchase orders sent to vendors
- Receiving reports showing what goods arrived
- Payment records and bank statements
Most businesses now receive these documents electronically, making them easier to organize and store. For example, PDF invoices received via email can be saved in a central digital location for easy access.
2. Matching Information
Next, compare the details on each document to check for consistency. This includes:
- Product or service descriptions
- Quantities ordered vs. received
- Unit prices and total amounts
- Dates and delivery terms
- Vendor information and payment terms
This step makes sure that what was ordered matches what was received and what was billed. For instance, if you ordered 50 office chairs at $100 each but the invoice shows 55 chairs, you’d need to look into this difference.
3. Identifying Discrepancies
During the matching process, look for any differences between documents. Common discrepancies include:
- Price variances between purchase orders and invoices
- Quantity differences between receiving reports and invoices
- Missing or additional items on invoices
- Duplicate invoices or payments
- Mathematical errors in calculations
A good practice is to flag any discrepancies right away so they can be looked into further. For example, if the unit price on an invoice is $25 but your purchase order shows $22, this variance should be noted for review.
4. Investigating Issues
For each discrepancy found, conduct a thorough investigation to find the cause. This might involve:
- Checking with the purchasing department about price changes
- Confirming with the receiving department about actual quantities
- Reviewing contract terms for price agreements
- Contacting vendors for clarification
Documentation is key during this step. Keep records of all communications and findings to support any decisions made. For instance, if a vendor confirms a price increase was approved but not updated in your system, note this explanation.
5. Resolving Discrepancies
After finding the cause of each discrepancy, take steps to resolve it:
- For vendor errors, request a corrected invoice
- For internal errors, update your records
- For approved variances, document the approval
- For disputed charges, work with vendors to reach an agreement
This step ensures that all parties agree on the final amount to be paid. For example, if a vendor mistakenly billed for 100 items when only 80 were ordered and received, you would request a corrected invoice before making payment.
6. Recording Transactions
Once all discrepancies are resolved, record the final transaction in your accounting system:
- Enter the correct invoice amount
- Link it to the corresponding purchase order
- Note any adjustments made
- Update vendor payment schedules
Accurate recording helps maintain clean financial records. For instance, if an invoice was adjusted from $5,000 to $4,500 after reconciliation, your accounting system should reflect the correct $4,500 amount.
7. Authorizing Payments
The final step is getting approval to pay the verified invoice:
- Submit reconciled invoices for payment approval
- Include documentation of any resolved discrepancies
- Follow your company’s payment authorization process
- Schedule payment according to terms
This process ensures that only verified, accurate invoices are paid. For example, after invoice processing for $10,000 worth of raw materials matches the purchase order and receiving report, the accounts payable manager would approve it for payment according to the vendor’s payment terms.
Types of Invoice Reconciliation
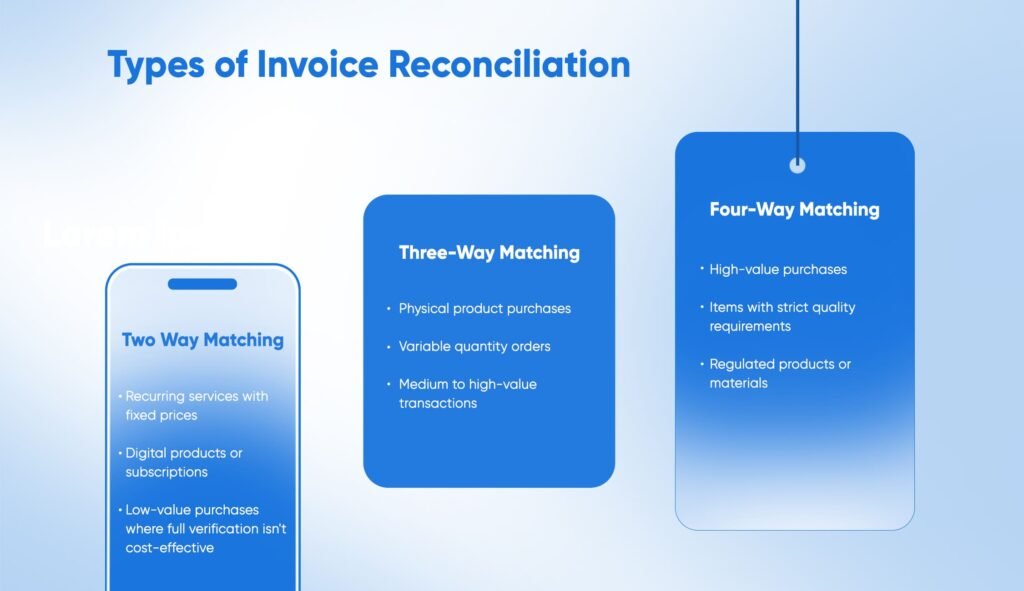
There are several methods of invoice reconciliation, each offering different levels of verification based on the complexity and value of purchases. Understanding these types helps you choose the right approach for different situations.
Two-Way Matching
Two-way matching compares just two documents: the purchase order and the invoice. This basic form of reconciliation checks if what was ordered matches what was billed.
This method works well for:
- Recurring services with fixed prices
- Digital products or subscriptions
- Low-value purchases where full verification isn’t cost-effective
For example, a monthly software subscription would be a good candidate for two-way matching. You would verify that the monthly invoice amount matches your subscription agreement before payment.
Two-way matching is simple but less thorough than other methods. It doesn’t verify that goods or services were actually received, which can be a risk for physical products.
Three-Way Matching
Three-way matching in accounts payable adds an extra layer of verification by comparing three documents: the purchase order, the receiving report, and the invoice. This method confirms not only that what was ordered matches what was billed, but also that it was actually received.
This approach is good for:
- Physical product purchases
- Variable quantity orders
- Medium to high-value transactions
For instance, when ordering office furniture, three-way matching would verify that the 20 desks ordered match both the quantity on the invoice and the quantity noted as received on the delivery report.
Three-way matching is the most common reconciliation method for most businesses. It provides a good balance between thorough verification and practical efficiency.
Four-Way Matching
Four-way matching adds yet another verification step by including inspection results along with the purchase order, receiving report, and invoice.
This intensive method ensures that items not only arrived but also meet quality standards.
This method is best for:
- High-value purchases
- Items with strict quality requirements
- Regulated products or materials
For example, when purchasing electronic components for manufacturing, four-way matching would verify the order, receipt, and invoice, plus confirm that the components passed quality testing before approving payment.
While four-way matching offers the highest level of verification, it also requires the most time and resources. Most companies reserve this method for their most critical or expensive purchases.
Vendor Statement Reconciliation
This type of reconciliation involves comparing your records of all transactions with a vendor against the vendor’s statement of your account. It helps catch any missed invoices, duplicate payments, or credits that weren’t applied.
Vendor statement reconciliation is typically done monthly or quarterly and serves as a good check of your overall reconciliation process.
For example, a monthly review of your office supply vendor’s statement might reveal an invoice that never made it into your system, allowing you to prevent a future past-due notice.

Why Invoice Reconciliation Matters for Businesses?
Invoice reconciliation affects multiple aspects of a business beyond just accounting. Understanding these impacts helps show why this process deserves attention and resources.
Financial Accuracy
Proper reconciliation ensures that financial statements correctly reflect business expenses. When invoices are reconciled before payment, companies avoid:
- Overpayments for goods not received
- Paying incorrect amounts due to pricing errors
- Duplicate payments for the same goods or services
For example, a construction company that properly reconciles material invoices can ensure its project cost tracking is accurate, leading to better pricing and profitability analysis for future projects.
Accurate financial records also support better business decisions. When expenses are correctly recorded, budget planning and financial forecasting become more reliable.
Fraud Prevention
Invoice reconciliation serves as a key defense against both internal and external fraud. According to the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners, billing schemes are among the most common types of fraud.
Through careful matching of documents, businesses can spot red flags such as:
- Invoices from fake vendors
- Charges for goods never ordered or received
- Inflated prices or quantities
- Multiple payments for the same invoice
A retail chain that implements thorough invoice reconciliation might catch an attempt to bill for store fixtures that were never delivered, saving thousands of dollars in fraudulent charges.
Regular reconciliation creates an environment where fraud is harder to commit and easier to detect, protecting company assets.
Cash Flow Management
Effective invoice reconciliation helps businesses manage cash flow more precisely. By ensuring that only valid invoices are paid and that they’re paid at the right time, companies can:
- Avoid unexpected cash outflows from error correction
- Take advantage of early payment discounts when appropriate
- Plan payment timing based on accurate liability information
- Prevent late payment penalties from missed invoices
A manufacturing company with good reconciliation practices can better schedule payments to vendors based on accurate information about what’s actually due and when, helping maintain optimal cash reserves.
Vendor Relationships
Good invoice reconciliation practices lead to smoother vendor relationships. When payments are accurate and timely, vendors are more likely to:
- Continue providing good service
- Offer favorable terms
- Resolve issues quickly
- Prioritize your orders during supply constraints
For instance, a restaurant that consistently reconciles food supplier invoices and pays correctly builds trust with those suppliers, potentially leading to better pricing or priority delivery during shortages.
Conversely, constant payment disputes due to poor reconciliation can harm these relationships, potentially affecting your supply chain.
Invoice Reconciliation Best Practices
Implementing these best practices can help make your invoice reconciliation process more efficient and accurate, reducing errors and saving time.
Establish Clear Policies and Procedures
Create and document standard procedures for invoice reconciliation:
- Define roles and responsibilities for each step
- Set clear approval thresholds and authorities
- Establish communication protocols for discrepancies
- Create documentation standards for record-keeping
For example, your policy might specify that the purchasing manager must approve all price variances over 5%, while accounts payable can resolve smaller discrepancies directly with vendors.
These documented procedures like document archiving ensure consistency. They provide guidance when questions arise. They also help new employees learn the process more quickly.
Implement Regular Reconciliation Schedules
Set up and follow a consistent schedule for reconciliation activities:
- Daily review of new invoices
- Weekly matching and discrepancy resolution
- Monthly vendor statement reconciliation
- Quarterly review of the entire process
A consistent schedule helps prevent backlogs and ensures issues are caught early. For instance, daily invoice review might catch a duplicate bill before payment is made, while monthly statement reconciliation could identify a missed credit that should have been applied.
Use Automation Tools
Leverage technology to make reconciliation more efficient:
- Invoice scanning and data extraction software
- Automated matching algorithms
- Electronic workflow for approvals
- Integration between purchasing and accounting systems
A mid-sized company might use automation to extract data from PDF invoices and automatically match it against purchase orders in their system, flagging only the exceptions that need human review.
Train Staff Properly
Ensure that all involved employees understand both the process and its importance:
- Provide initial training on reconciliation procedures
- Offer refresher sessions when processes change
- Share common error examples and how to avoid them
- Explain the business impact of accurate reconciliation
For example, training sessions might show accounting staff how to properly compare unit prices that might be expressed differently on purchase orders versus invoices (such as per-item versus per-case pricing).
Monitor and Improve the Process
Regularly assess your reconciliation process and look for ways to make it better:
- Track key metrics like error rates and resolution time
- Gather feedback from staff involved in the process
- Look for patterns in discrepancies to address root causes
- Update procedures based on findings
A company might notice that invoices from a particular vendor frequently have quantity discrepancies, leading to a conversation with that vendor about improving their order fulfillment process.
Maintain Proper Documentation
Keep thorough records of all reconciliation activities:
- Save all supporting documents
- Document resolution of discrepancies
- Maintain an audit trail of approvals
- Organize records for easy retrieval
Good documentation not only supports audit requirements but also helps resolve any questions that might arise later.
For instance, if a vendor claims a disputed invoice was actually correct, you can retrieve the documentation showing why adjustments were made.
Manual vs. Automated Invoice Reconciliation
Depending on your team size and transaction volume, reconciliation may be manual or automated.
Manual Reconciliation
Often used by small businesses. It relies on human review.
- Lower cost to start
- Higher error risk
- Slower processing time
Automated Reconciliation
Used by growing teams and enterprise finance departments.
- Scans invoices and matches fields automatically
- Supports bulk processing and exception alerts
- Keeps logs for audits and analytics
Automation reduces time spent on low-value tasks and improves consistency.
Invoice Reconciliation Challenges and Solutions
Despite its importance, invoice reconciliation comes with several challenges. Here are some common issues and practical solutions to help address them.
Challenge: High Volume of Invoices
Many businesses struggle to keep up with a large number of invoices coming from multiple vendors, making thorough reconciliation time-consuming.
Solutions:
- Prioritize reconciliation based on value and risk
- Use automation tools to handle routine matching
- Consider a dedicated reconciliation team for high-volume periods
- Implement vendor portals where suppliers enter invoice data directly
For example, a retail chain might use automated matching for 80% of their invoices, focusing manual review only on high-value purchases or vendors with a history of errors.
Challenge: Data Quality Issues
Poor data entry, inconsistent formats, and missing information can make matching difficult and time-consuming.
Solutions:
- Standardize document formats across the organization
- Implement data validation at entry points
- Use OCR technology with validation rules
- Work with vendors on standardizing invoice formats
A manufacturing company might provide vendors with a standard invoice template that includes all required fields in a consistent format, reducing data quality issues.
Challenge: Process Delays
Delays in document classification, approvals, and issue resolution can slow down the entire reconciliation process.
Solutions:
- Implement electronic workflows with automatic routing
- Set clear timeframes for each step in the process
- Use alerts for pending approvals and approaching deadlines
- Create escalation procedures for stalled items
For instance, an automated system could send daily reminders to managers with invoices awaiting approval, with escalation to their supervisor after three days of no action.
Challenge: Limited Visibility
Without good tracking, it can be hard to know where invoices stand in the reconciliation process.
Solutions:
- Use a central dashboard showing the status of all invoices
- Implement tracking codes for different stages
- Provide real-time updates to stakeholders
- Generate regular status reports
A dashboard might show finance leaders that 85% of invoices are reconciled within two days, but purchases from international vendors take an average of five days, helping identify areas for improvement.
Challenge: Compliance Requirements
Many industries have specific regulations about financial controls and record-keeping that affect reconciliation procedures.
Solutions:
- Stay informed about relevant regulations
- Build compliance requirements into standard procedures
- Conduct regular audits of the reconciliation process
- Work with compliance experts when needed
A healthcare provider might implement special verification steps for medical equipment purchases to comply with both financial and patient safety regulations.
Why Should You Choose KlearStack for Invoice Reconciliation?
Financial teams need dependable tools for invoice reconciliation. Your current manual processes might be slow and error-prone. KlearStack changes how your finance department handles invoice verification and payment approvals.
Solutions That Matter:

- Template-free processing that works with any invoice format
- Self-learning AI that gets better with each document processing task
- End-to-end automation reducing manual data entry by 85%
Proven Performance in Finance:
Processing Speed: Handle thousands of invoices daily with consistent accuracy Multi-Format Support: Process any invoice type without custom templates Accuracy Guarantee: Achieve up to 99% extraction accuracy across all documents
Your finance team needs smart invoice reconciliation. KlearStack is one of the most accurate invoice processing solutions available. The system gets smarter with each document it processes, improving verification accuracy over time.
Key Processing Capabilities:
- Intelligent field extraction from varying invoice layouts
- Automated data validation and matching
- Secure document handling meeting financial compliance standards
Smart finance departments need smart solutions. KlearStack can reduce your invoice processing time by 80%.
Ready to make your invoice reconciliation process more accurate and efficient?

Conclusion
Invoice reconciliation is a vital process for financial accuracy and fraud prevention. It helps businesses verify that what they pay matches what they ordered and received.
- Implementing proper reconciliation can reduce payment errors by up to 80%
- Regular reconciliation helps catch issues before they become major problems
- The right level of verification depends on the value and risk of each purchase
- Automation can transform a time-consuming process into an efficient system
The benefits of good invoice reconciliation extend beyond the finance department, helping with cash flow, vendor relationships, and overall business performance. The time invested in setting up proper reconciliation processes pays off through improved financial control and reduced risk.
FAQ on Invoice Reconciliation
Invoice reconciliation is the process of matching invoices with purchase orders and receiving reports. It verifies that what you ordered matches what you received and what you were billed for.
Most businesses should reconcile invoices daily or weekly. Regular schedules help catch errors early and prevent backlogs of unprocessed invoices.
The main benefits include preventing overpayments, catching fraud, reducing errors, and maintaining accurate financial records. Good reconciliation also helps build better vendor relationships.
Yes, even small businesses can benefit from basic invoice automation. Simple tools can reduce manual work and errors while providing better visibility into spending.


