How to Do a Bank Reconciliation [In 8 Easy Steps]? Guide for Accurate Accounting
![How to Do a Bank Reconciliation [In 8 Easy Steps]? Guide for Accurate Accounting](https://lightgrey-antelope-914579.hostingersite.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/How-to-Do-a-Bank-Reconciliation-In-8-Easy-Steps-Guide-for-Accurate-Accounting.jpg)
No less than 45% of small businesses in the U.S. have issues with cash flow (QuickBooks Small Businesses Annual Report). Most of these cash flow problems are caused by delayed reconciliations or record entry errors.
Bank reconciliation means, matching your business records with the bank statement to spot errors early. Not doing regular checks might result in fraud or missing entries.
Consider thinking over the following questions:
- Can your finance team identify transaction mistakes instantly?
- Are hidden bank charges frequently missed in your books?
- How reliably does your reconciliation prevent financial mistakes?
Don’t fix these errors and watch your business blueprint go down the rails. Regular reconciliation basically, keeps financial records transparent and dependable.
Key Takeaways
- Compare your bank statement line-by-line with internal records.
- Identify and record outstanding checks and pending deposits.
- Make adjustments to match records with the bank balance.
- Regular reconciliation helps prevent financial errors.
- Automation simplifies reconciliation tasks, reducing errors.
What is Bank Statement Reconciliation?

Bank statement reconciliation compares your accounting records directly with the bank’s records. A reconciled bank statement neatly verifies each transaction, finding mistakes beforehand. If done accurately, reconciliation protects your cash flow and reduces fraud risks.
A good and trustable financial management needs consistent reconciliation. Let’s examine the steps to reconcile your bank statement effectively.
With the rise of automation, organizations no longer need to do it manually. In fact, you can reconcile multiple statements at high speed and scale with automation tools like KlearStack. How? Through the method of automated document processing these solutions can remove manual processing completely.
Step-by-Step Guide to Reconcile a Bank Statement
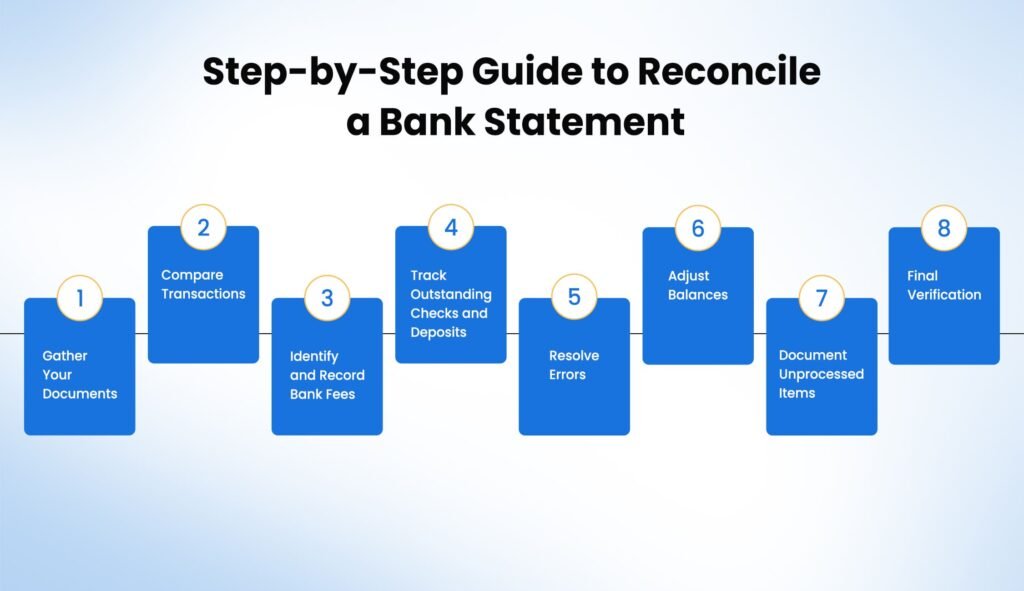
Step 1: Gather Your Documents
Begin by collecting your bank statements and business accounting records. These documents must be up-to-date and well-organized. Organized documents reduce confusion and errors during reconciliation.
Step 2: Compare Transactions
Match each deposit and withdrawal on your bank statement with your accounting records carefully. Note down any mismatches immediately. Quick identification of differences simplifies the reconciliation.
Step 3: Identify and Record Bank Fees
Bank charges often appear on statements without prior notice. Add these fees to your business records. Timely recording of fees improves financial clarity.
Step 4: Track Outstanding Checks and Deposits
Identify checks and deposits not yet processed by your bank. Note these neatly in your records. This prevents future discrepancies and ensures accurate balances.
Step 5: Resolve Errors
Investigate discrepancies to check if balances still differ. Fix incorrect entries or contact the bank if needed. Quickly correcting these errors maintains accurate financial records.
Step 6: Adjust Balances
After carefully identifying differences, adjust your records accordingly. Add deposits in transit and subtract outstanding checks. This adjustment aligns all your balances in order.
Step 7: Document Unprocessed Items
List down any uncleared checks or deposits in transit. Tracking these items prevents future reconciliation mistakes and maintains financial accuracy.
Step 8: Final Verification
Conduct a final check ensuring adjusted balances match precisely. Confirm all adjustments are accurate. This final verification ensures accurate financial data.
How Often Should You Reconcile Bank Statements?
Businesses should reconcile bank statements monthly. Companies with more frequent transactions should consider weekly reconciliations. Regular checks improve accuracy and detect errors quickly.
Monthly reconciliation ensures smaller issues do not become larger problems over time. Additionally, regular reconciliation allows your business to stay aware of its actual cash position, improving your ability to make informed financial decisions.
Companies with high transaction volumes will benefit from weekly or daily reconciliation. It quickly identifies errors or unusual activities. This frequency can help manage cash flow more effectively, ensuring funds are accurately tracked and available when needed.
Doing timely reconciliation also helps better financial management practices. It can increase accountability and improve internal controls. Regular reconciliation helps businesses to detect fraud earlier and take appropriate measures.
Common Mistakes in Bank Reconciliation

Overlooking minor bank fees can turn into long-term problems over time. It will complicate reconciliation processes. Duplicate or incorrect transaction entries cause unnecessary confusion and delays in final reconciliation records.
Avoid these reconciliation mistakes:
- Missing small bank fees.
- Duplicate or incorrect entries.
- Ignoring outstanding checks.
- Starting with inaccurate opening balances.
Regularly addressing these issues improves management. Ignoring outstanding checks leads to wrong cash balances, creating confusion on available funds. Starting with an incorrect opening balance shakes the entire reconciliation process.
It can make it impossible to match your records accurately. Additional common mistakes include neglecting regular reconciliation schedules and inadequate documentation of adjustments.
These oversights can cause errors that can remain unnoticed for long intervals. Ensuring detailed documentation and regular review of reconciliation processes will minimize these risks by a big margin.
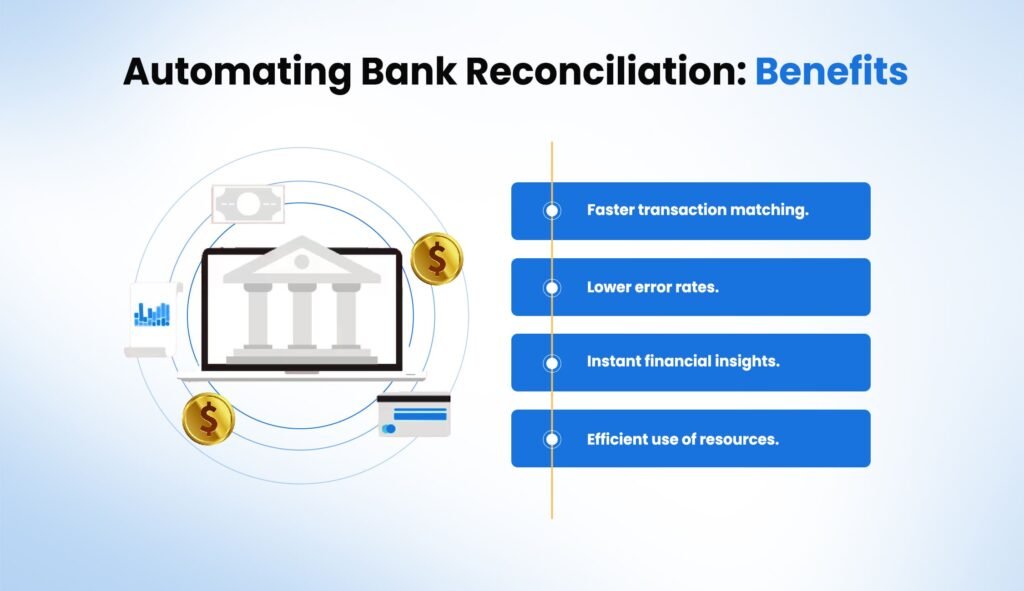
Automating Bank Reconciliation: Benefits
Automation reduces human error and creates more precise and reliable records. Moreover, automation tools provide real-time insights, allowing businesses to quickly identify and rectify issues.
With automated reconciliation, you also ensure consistent compliance with the right standards. You will be maintaining thorough audit trails without errors.
Automated reconciliation provides the following benefits:
- Faster transaction matching.
- Lower error rates.
- Instant financial insights.
- Efficient use of resources.
By the use of automation, businesses save considerable time that was spent on manual checking. It will free up resources for other financial activities. Automated reconciliation processes improve your organization’s ability to manage its financial activities confidently.
Why should you consider Automation of Bank Reconciliation?
Modern steps to reconcile a bank statement include automated solutions. Your organization can transform manual processes into simple operations. This shift speeds up processes while reducing the time spent on routine tasks.
Implementing bank statement reconciliation automation should be considered by all financial teams. It gives your team the time for detailed analysis instead of manual data entry. The system maintains consistent checking procedures across all transactions.
A reconciled bank account through automation offers better security as well. Your financial data receives systematic verification without manual intervention. This consistent checking helps prevent fraud and errors.
The reconciliation in banking process benefits from technological advancement. Your organization gains improved visibility into financial operations. Advanced systems provide real-time insights into your financial position.
Why Should You Choose KlearStack?
Among various bank reconciliation solutions available, KlearStack’s intelligent document processing has up to 99% precision in handling financial documents.
As a specialist in automated financial processing, KlearStack transforms how organizations handle bank reconciliation bank statement tasks.
When reconciling bank statements, KlearStack’s AI capabilities ensure exceptional accuracy. Your finance team benefits from automated data extraction that maintains consistency while reducing manual effort. This systematic approach strengthens your reconciliation process.

KlearStack’s Reconciliation Advantages:
- Processing Volume: Handles 10,000+ documents daily with consistent reliability
- Multi-format Support: Works with bank PDFs, CSVs, or even scanned images
- Accuracy Score: Achieves 99% extraction accuracy across varying layouts
How to reconcile a bank statement changes fundamentally with KlearStack’s technology. Your finance team can:
- Preview the solution using your actual bank statements
- Discuss specific reconciliation challenges and solutions
- Plan implementation that matches your financial processes
Whether you need to improve reconciliation accuracy, reduce processing time, or strengthen financial controls, KlearStack provides the tools for efficient bank reconciliation bank statement processing.
Experience how KlearStack transforms your reconciliation in banking processes with intelligent automation.
Conclusion
Accurate reconciliation maintains financial transparency. It reduces errors, prevents fraud, and simplifies audits.
Business Impacts:
- Increases financial accuracy
- Reduces manual efforts
- Improves financial decision-making
Reliable reconciliation supports strong business growth.
FAQ’s on How to Do a Bank Reconciliation?
Compare your bank statement with accounting records. Adjust entries to fix any discrepancies found.
Investigate immediately for missing or incorrect entries. Adjust records or contact your bank quickly.
Reconcile monthly for accurate results. Businesses with frequent transactions should reconcile weekly.
Automation reduces human mistakes significantly. It speeds up reconciliation.


